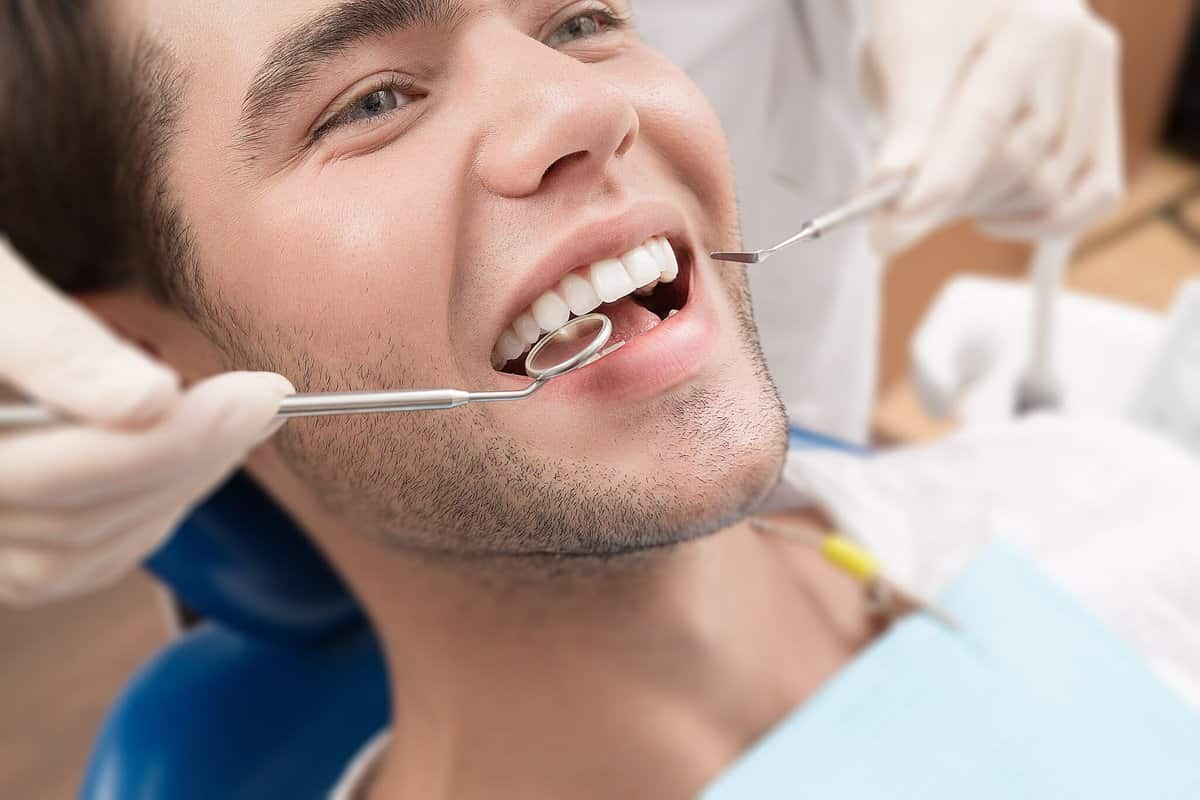
آلوئولوپلاستی
عمل جراحی که جهت تغییر شکل دادن قسمت هایی از فک که دندان های آن از بین رفته است , آلوئولوپلاستی نام دارد. آلوئول بخشی از استخوان فک می باشد که دندان ها را در خود جای داده است.صاف کردن استخوان فک , روشی بسیار مناسب و ضروری برای قرار گیری دندان های مصنوعی در دهان می باشد.
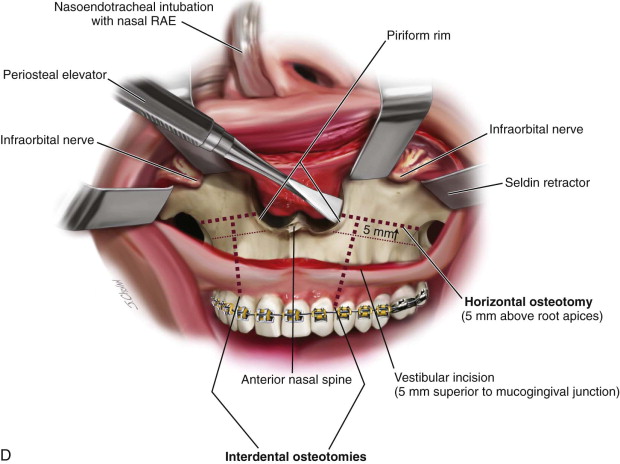
آلوئولوپلاستی (استئوتومی) فکی – دندانی:(جراحی اصلاح فک ) جراحی ای است که در آن استخوان ها برای اصلاح بد شکلی فکی – دندانی برش داده می شوند تا جا به جا، تغییر و باز تنظیم شوند. کلمه Osteotomy به معنی تقسیم یا برداشتن و برش استخوان است. این عملیات برای اصلاح مشکلات فکی که با ناهنجاری های فکی – دندانی مواجه هستند استفاده می شود.
ناهنجاری هایی مانند پروگناتیسم یا جلو و بزرگ بودن فک بالا یا پایین، اوپن بایت، درد و اختلالات مفصل گیجگاهی فکی و همچنین عقب رفتگی چانه. رشد نامتناسب فک بالا یا پایین باعث تغییر شکل فک و دندان ها می شود ، رشد نامتناسب فک در این حالت جویدن مواد غذایی را مشکل می کند و هم چنین ممکن است باعث درد شود چراکه عضله و اسخوان فک تحت فشار قرار دارند.
روش عمل آلوئولوپلاستی
اکثر آلوئولوپلاستی (استئوتومی) فکی – دندانی تحت بیهوشی عمومی انجام می گردد. بیهوشی عمومی به جراحان اجازه می دهد تا عمل استئوتومی فکی – دندانی را به طور موثر و بدون حرکت غیر ارادی عضلانی و درد انجام دهند.
به منظور کاهش احتمال عفونت قبل از هرگونه جراحی، دندان مولر سوم (دندان عقل ) بویژه در فک پایین باید خارج شود.
Jaw-tooth osteotomy incisions are made using swinging saws and reciprocating saws. Direct reciprocating saws are used for direct cutting of bone. Angled oscillating saw with which a special angular osteotomy can be performed, such as lowering the angle of the mandible.
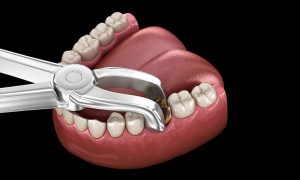
چه زمانی آلوئوپلاستی لازم است؟
همه کسانی که دندان خود را از دست داده اند و به دنبال تعویض دندان هستند نیاز به آلوئولوپلاستی ندارند. اگر شکل فک برای حمایت از ترمیم رضایت بخش باشد، دیگر نیازی به تغییر شکل نیست.
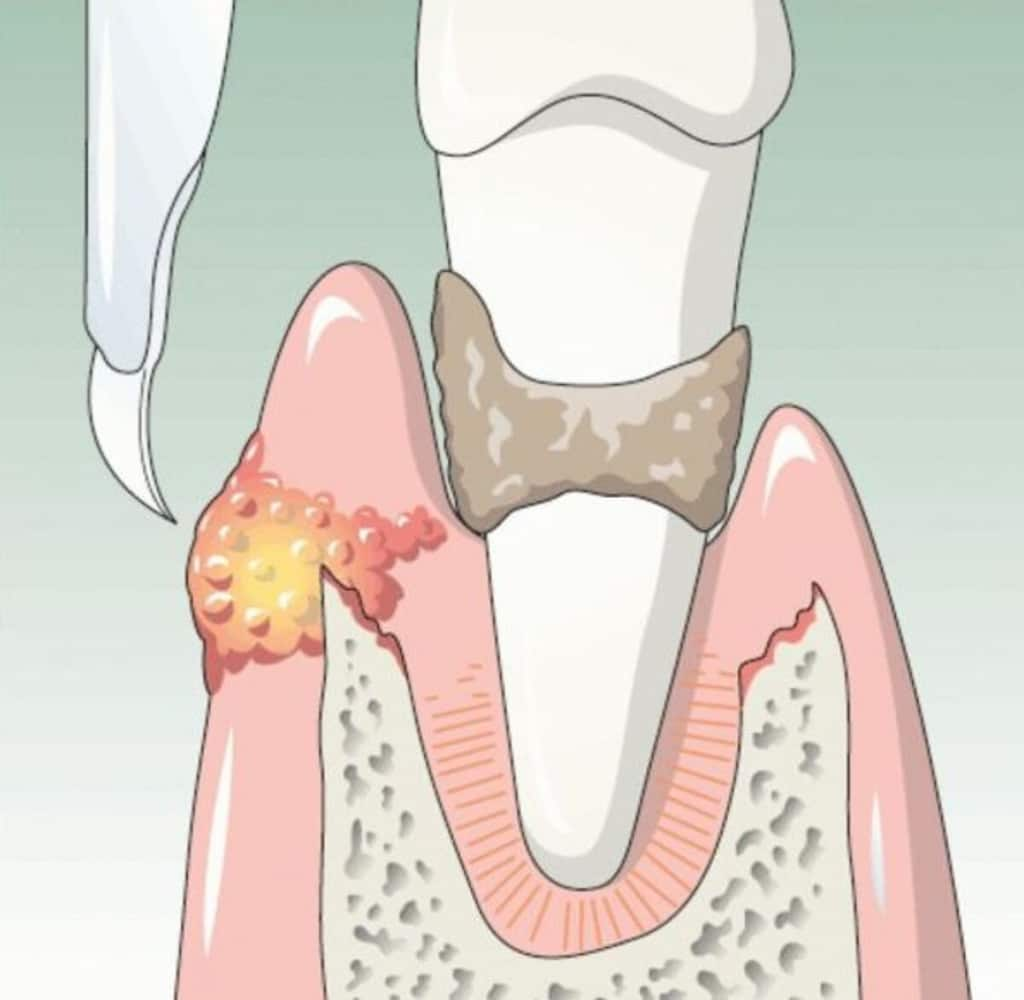
با این حال، ظاهر شدن برجستگیهای ناهموار که میتواند باعث ناراحتی، حساسیت یا ترمیم نامناسب شود اگر روی سطح ناهموار قرار گیرد، غیرمعمول نیست. آلوئولوپلاستی را می توان در هر زمانی انجام داد – در لحظه کشیدن پس از بهبود محل کشیدن دندان یا مدت طولانی پس از از دست دادن دندان.
با این حال، انجام آن همراه با استخراج معمول است زیرا باعث بهبودی می شود، خطر خشکی حفره را کاهش می دهد، نیاز به روش دوم را از بین می برد و هزینه ها را کاهش می دهد.
دندانپزشکی که کشیدن شما را انجام می دهد، شکل فک شما را ارزیابی می کند تا مشخص کند که آیا نیاز به اصلاح مجدد دارد یا خیر. اگر تصمیم بگیرید که برای انجام این روش تا زمان بهبودی صبر کنید، روند جایگزینی دندان طولانی خواهد شد. بهبود سریع آلوئولوپلاستی برای بیماران سرطانی که تحت پرتودرمانی قرار می گیرند و کسانی که از بیماری های خود ایمنی رنج می برند مهم است.
هزینه عمل آلوئولوپلاستی
برای مشاوره تخصصصی و اطلاع از قیمت با متخصصان ما در Dental Clinic Alma تماس بگیرید.
شماره تماس: 02166916624
هدف از آلوئولوپلاستی
هنگامی که از کشیدن دندان بهبود یافتید ، ممکن است یک برجستگی آلوئولی ناهموار یا ناهموار داشته باشید که سطح ناهمواری را ایجاد می کند که برای حمایت از ترمیم دندان ایده آل نیست. برای آماده سازی دهان برای کاشت دندان، ممکن است لازم باشد استخوان فک را صاف کنیم. این امر عوارض را کاهش می دهد و اگر این عمل در زمان کشیدن دندان انجام شود، می تواند به روند بهبودی کمک کند.
چه چیزی در عمل آلوئولوپلاستی نقش دارد؟
این یک روش جراحی است که در آن ما استخوان فک شما را برای ایجاد یک سطح صاف تغییر شکل می دهیم. نام این روش از استخوان آلوئول گرفته شده است. هدف از این روش ایجاد سطحی صاف، گسترده و یکنواخت برای روشهای دهانی آینده است.
آیا آلوئولوپلاستی خطرناک است؟
نه، این یک روش خطرناک نیست، اما مانند هر جراحی، شما باید توصیه های خاصی را برای اطمینان از بهبودی مناسب و جلوگیری از عفونت دنبال کنید.
آلوئولوپلاستی همراه با اکستنشن چیست؟
آلوئولوپلاستی ساده را می توان همراه یا بعد از کشیدن دندان انجام داد. معمولاً برای از بین بردن لبه های تیز در سوکت دندان ها در نظر گرفته شده است. این یک روش لازم برای آماده سازی برای توانبخشی پروتز است تا ایمپلنت های دندانی ماندگاری و ثبات بیشتری داشته باشند.
آلوئولوپلاستی چقدر طول می کشد؟
عمل جراحی معمولاً حدود یک ساعت طول می کشد و می توان آن را به عنوان بخشی از سایر درمان ها یا به تنهایی انجام داد.
جراحی آلوئولوپلاستی چگونه انجام می شود؟
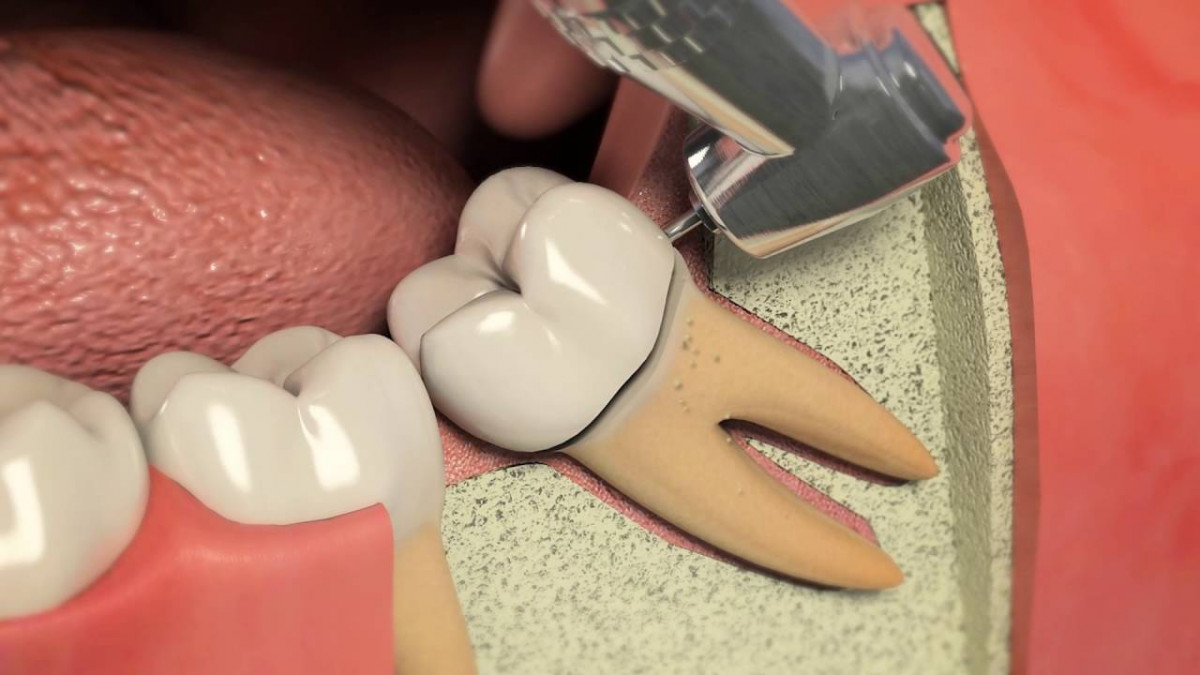
بیماران با یک بی حس کننده موضعی بیهوش می شوند تا مطمئن شوند که درمان بدون درد است. سپس برشی در خط لثه ایجاد می شود تا استخوان فک زیرین نمایان شود. هنگامی که استخوان بیش از حد در معرض دید قرار گرفت، از ابزارهای جراحی برای صاف کردن و تنظیم استخوان به شکل دلخواه استفاده می کنیم. هنگامی که کانتور مناسب به دست آمد، منطقه به طور کامل آبیاری می شود و بافت به جای خود باز می گردد. بخیه ها برای اطمینان از موقعیت و امکان بهبودی مناسب قرار داده می شوند.
Recovery time:
بهبود اولیه تمام استئوتومی های دندانی نیاز به 2 تا 6 هفته زمان دارند. بهبودی ثانویه 2 تا 4 ماه بعد از زمان بهبودی اولیه صورت می گیرد. در نهایت اگر برش های فک توسط پیچ هایی ثابت شده باشند ، به طور معمول در طی دوره بهبودی 2 تا 3 ماه استخوان ها آن ها را خواهند پوشاند.
جمع بندی
تا اینجا سعی کردیم اطلاعات مناسنی در مورد عمل آلوئوپلاستی به شما دوستان عزیز بدهیم برای کسب اطلاعات بیشتر با متخصصان ما در کلینیک دندانپزشکی آلما تماس بگیرید.
شماره تماس: 02166916624
Frequently Asked Questions
چه زمانی آلوئوپلاستی لازم است؟
همه کسانی که دندان خود را از دست داده اند و به دنبال تعویض دندان هستند نیاز به آلوئولوپلاستی ندارند. اگر شکل فک برای حمایت از ترمیم رضایت بخش باشد، دیگر نیازی به تغییر شکل نیست. با این حال، ظاهر شدن برجستگیهای ناهموار که میتواند باعث ناراحتی، حساسیت یا ترمیم نامناسب شود اگر روی سطح ناهموار قرار گیرد، غیرمعمول نیست. آلوئولوپلاستی را می توان در هر زمانی انجام داد - در لحظه کشیدن پس از بهبود محل کشیدن دندان یا مدت طولانی پس از از دست دادن دندان.
آیا آلوئولوپلاستی خطرناک است؟
نه، این یک روش خطرناک نیست، اما مانند هر جراحی، شما باید توصیه های خاصی را برای اطمینان از بهبودی مناسب و جلوگیری از عفونت دنبال کنید.
جراحی آلوئولوپلاستی چگونه انجام می شود؟
بیماران با یک بی حس کننده موضعی بیهوش می شوند تا مطمئن شوند که درمان بدون درد است. سپس برشی در خط لثه ایجاد می شود تا استخوان فک زیرین نمایان شود. هنگامی که استخوان بیش از حد در معرض دید قرار گرفت، از ابزارهای جراحی برای صاف کردن و تنظیم استخوان به شکل دلخواه استفاده می کنیم. هنگامی که کانتور مناسب به دست آمد، منطقه به طور کامل آبیاری می شود و بافت به جای خود باز می گردد. بخیه ها برای اطمینان از موقعیت و امکان بهبودی مناسب قرار داده می شوند.




9 Responses
سلام وقتتون بخیر
هزینه جراحی آلوئولوپلاستی چقد راست؟
سلام وقتتون بخیر
عمل آلوئولوپلاستی چقدر طول میکشه؟
سلام وقت شما هم بخیر
عمل جراحی معمولاً حدود یک ساعت طول می کشد و می توان آن را به عنوان بخشی از سایر درمان ها یا به تنهایی انجام داد. جهت کسب اطلاعات بیشتر با متخصصان ما در کلینیک دندانپزشکی آلما تماس بگیرید. شماره تماس: ۰۲۱۶۶۹۱۶۶۲۴
سلام وقتتون بخیر
عمل آلوئولوپلاستی خطرناک هستش؟
سلام وقت شما هم بخیر
نه، این یک روش خطرناک نیست، اما مانند هر جراحی، شما باید توصیه های خاصی را برای اطمینان از بهبودی مناسب و جلوگیری از عفونت دنبال کنید.
جهت کسب اطلاعات بیشتر با متخصصان ما در کلینیک دندانپزشکی آلما تماس بگیرید. شماره تماس: ۰۲۱۶۶۹۱۶۶۲۴
سلام وقتتون بخیر
بعد از جراحی آلوئولوپلاستی چقدر زمان میبره تا بهبود پیدا کنیم؟
سلام وقت شما هم بخیر
بهبود اولیه تمام استئوتومی های دندانی نیاز به ۲ تا ۶ هفته زمان دارند. بهبودی ثانویه ۲ تا ۴ ماه بعد از زمان بهبودی اولیه صورت می گیرد. در نهایت اگر برش های فک توسط پیچ هایی ثابت شده باشند ، به طور معمول در طی دوره بهبودی ۲ تا ۳ ماه استخوان ها آن ها را خواهند پوشاند.
جهت کسب اطلاعات بیشتر با متخصصان ما در کلینیک دندانپزشکی آلما تماس بگیرید. شماره تماس: ۰۲۱۶۶۹۱۶۶۲۴
سلام وقتتون بخیر
هزینه جراحی آلوئولوپلاستی چقدر میشه؟
سلام وقت شما هم بخیر
جهت کسب اطلاعات بیشتر با متخصصان ما در کلینیک دندانپزشکی آلما تماس بگیرید. شماره تماس: ۰۲۱۶۶۹۱۶۶۲۴